Windows10系统下,在VSCode上配置C/C++运行环境。
写这篇文章的时候经历了两个阶段,所以会有一点断层,我尽量能将它完善好。
VSCode配置的方法目录:
使用VSCode装环境会涉及到一些配置文件,前几天使用VSCode配置了Python的环境,也涉及到了这部分,现在配置C/C++环境,同样需要配置。配置文件涉及到三个:launch.json、 c_cpp_properties.json、 tasks.json;他们的功能分别是:
- launch.json文件主要是用于配置调试器相关参数;
- tasks.json文件主要是用于配置编译器相关参数;
- c_cpp_properties.json文件主要是用于配置编译器路径和只能代码提示相关参数。
预先准备
在VSCode上安装C/C++扩展
-
在扩展一栏里面搜索C/C++,然后点击安装即可:
-
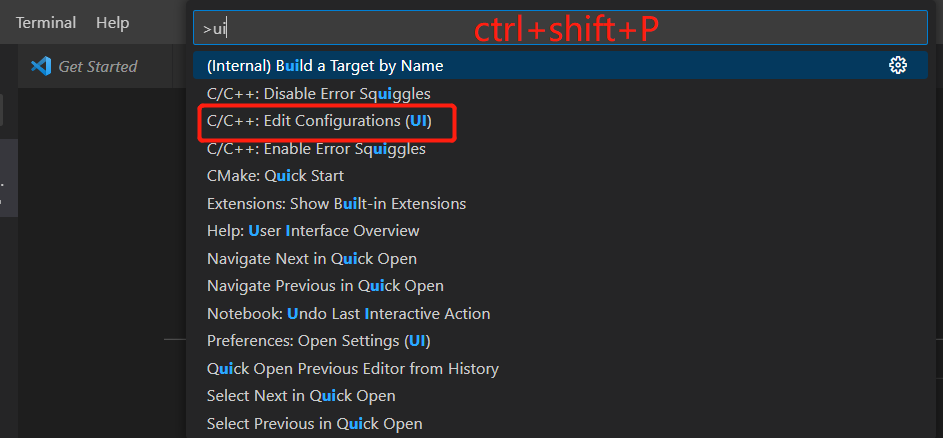
在C/C++扩展中进行配置:
ctrl+shift+P快捷键,然后输入“ui”即可找到该选项。
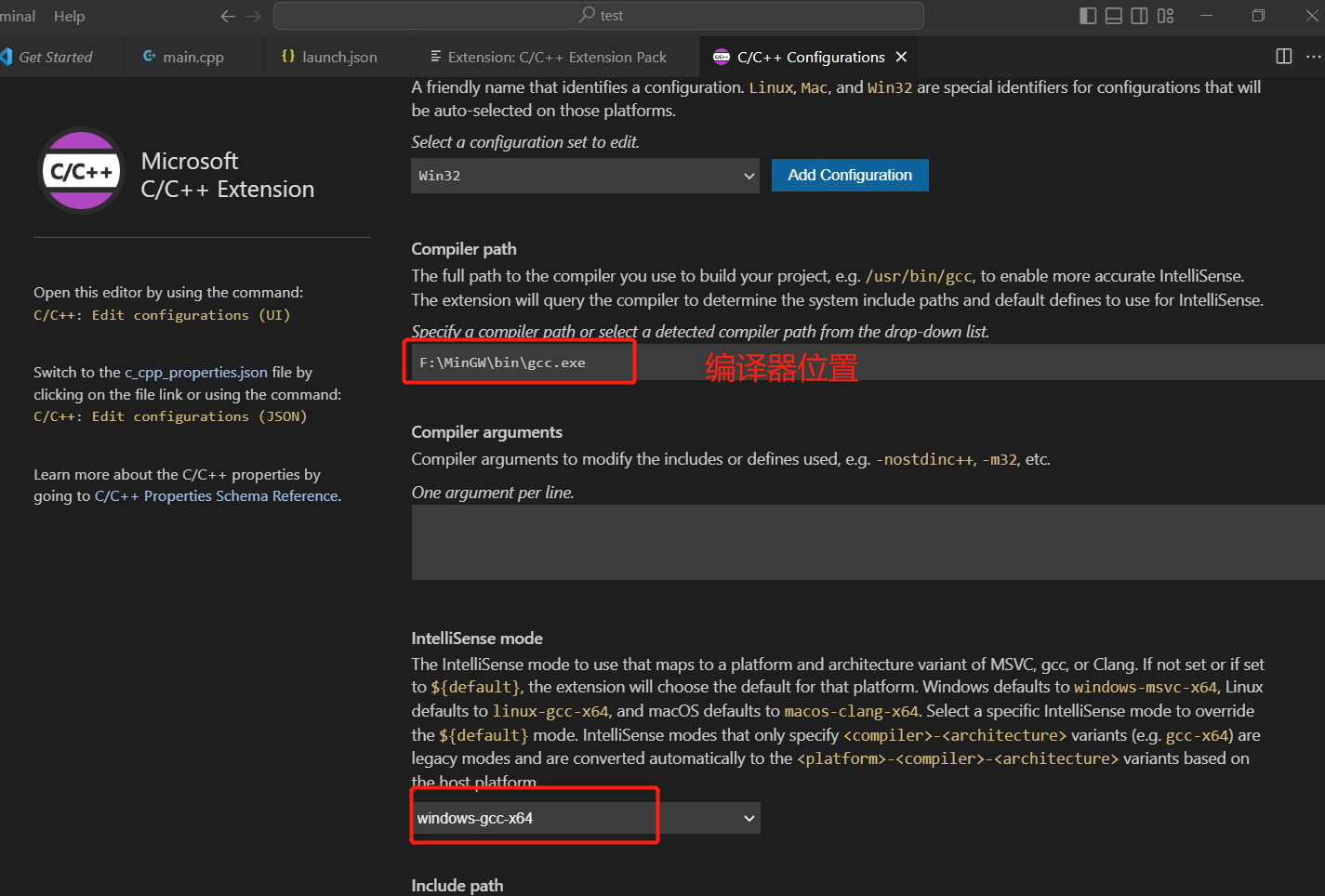
在C/C++扩展的UI界面配置编译器位置,以及合适的IntelliSence模式:
下载WinGW-w64
-
下载网址:https://sourceforge.net/projects/mingw-w64/files/mingw-w64/
-
文件区别:
文件清单
x86_64-posix-sjlj
x86_64-posix-seh
x86_64-win32-sjlj
x86_64-win32-seh
i686-posix-sjlj
i686-posix-dwarf
i686-win32-sjlj
i686-win32-dwarf释义1:
-
DWARF:一种带调试信息(DWARF- 2(DW2)EH)的包, 所以比一般的包尺寸大,仅支持32位系统
-
SJLJ:跨平台,支持32,64位系统,缺点是:运行速度稍慢,GCC不支持
-
SEH: 调用系统机制处理异常,支持32,64位系统,缺点是:Gcc不支持(即将支持)
释义2:
-
x86_64: 简称X64,64位操作系统
-
i686: 32位操作系统 (i386的子集),差不多奔腾2(1997年5月)之后的CPU都是可以用的
释义3:
-
posix: 启用了C++ 11 多线程特性
-
win32: 未启用 (从时间线上正在尝试也启用部分 Threading)
区别:
-
DWARF DWARF- 2(DW2)EH ,这需要使用DWARF-2(或DWARF-3)调试信息。 DW-2 EH可以导致可执行文件略显膨胀,因为大的调用堆栈解开表必须包含在可执行文件中。
-
setjmp / longjmp(SJLJ)。基于SJLJ的EH比DW2 EH慢得多(在没有异常时会惩罚甚至正常执行),但是可以在没有使用GCC编译的代码或没有调用堆栈的代码上工作。
-
结构化异常处理(SEH) (Structured Exception Handling)Windows使用自己的异常处理机制。
**注:上述对WinGW各种文件的解释来源于:https://www.pcyo.cn/linux/20181212/216.html **
-
-
选择合适的文件(离线安装的更快)下载,然后解压缩,并且将解压缩的地址下的bin目录添加到环境变量中:
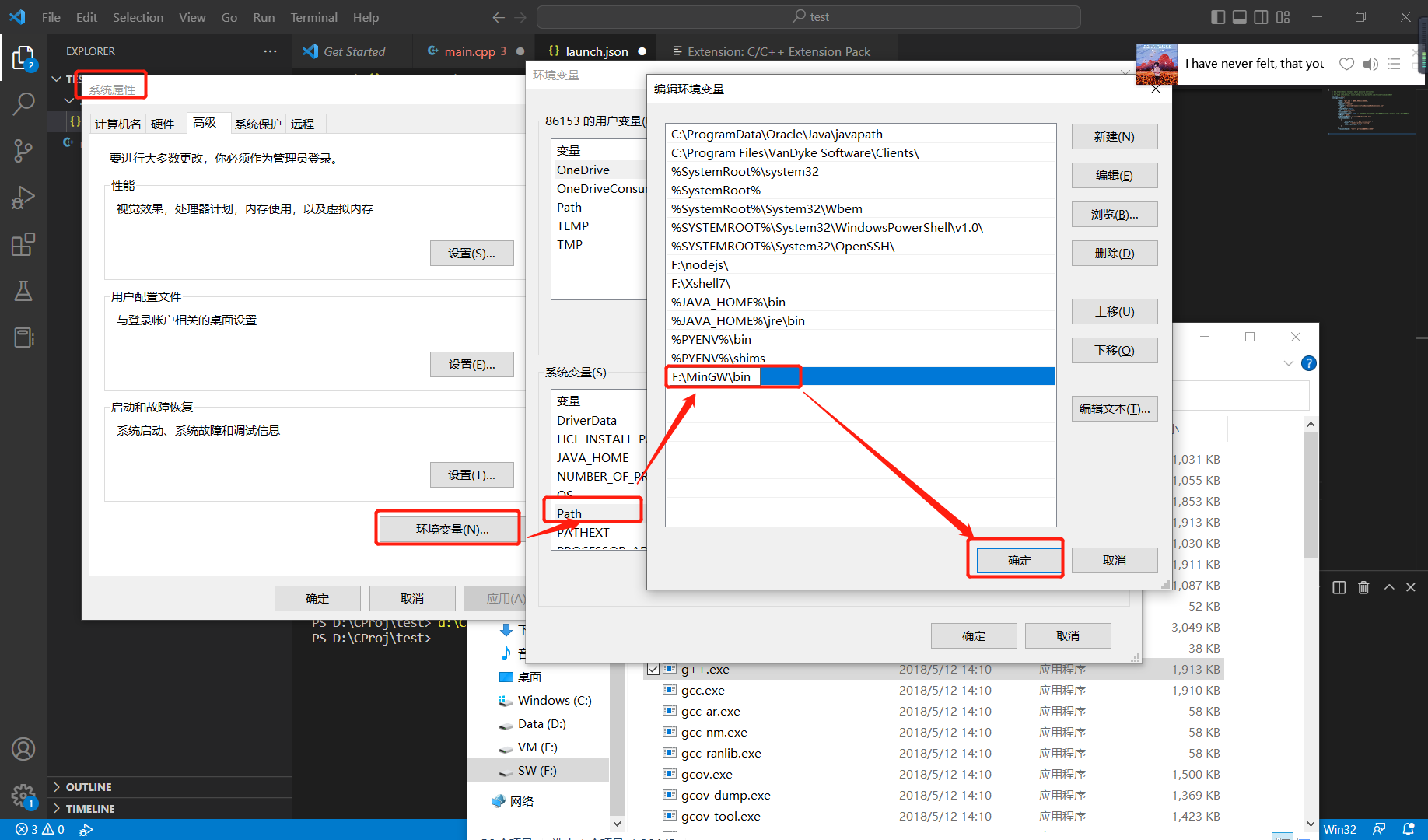
-
检测是否安装成功 ( 在CMD中测试 ):
g++ --version gdb --version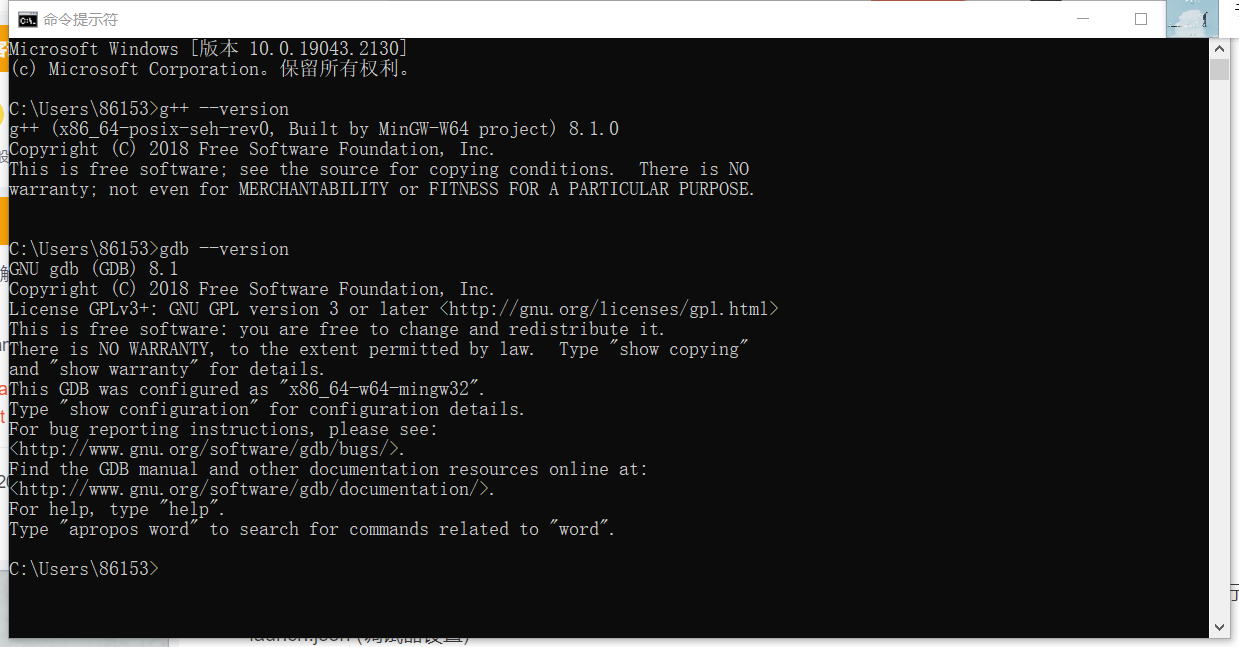
创建C/C++文件
在VSCode中关联一个工作目录(文件夹),该路径下会自动生成.vscode目录。创建一个cpp文件,在其中写一个hello world!的代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(){
printf("hello world!");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
**注意:这里添加 #include
配置方法
方法1:不使用VSCode插件
tasks.json文件:
// tasks.json
{
// https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/editor/tasks
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "Build", // 任务的名字叫Build,注意是大小写区分的,等会在launch中调用这个名字
"type": "shell", // 任务执行的是shell命令,也可以是
"command": "g++", // 命令是g++
"args": [
"'-Wall'",
"'-std=c++17'", //使用c++17标准编译
"'${file}'", //当前文件名
"-o", //对象名,不进行编译优化
"'${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe'", //当前文件名(去掉扩展名)
],
// 所以以上部分,就是在shell中执行(假设文件名为filename.cpp)
// g++ filename.cpp -o filename.exe
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
// 任务分组,因为是tasks而不是task,意味着可以连着执行很多任务
// 在build组的任务们,可以通过在Command Palette(F1) 输入run build task来运行
// 当然,如果任务分组是test,你就可以用run test task来运行
},
"problemMatcher": [
"$gcc" // 使用gcc捕获错误
],
}
]
}
launch.json文件:
里面主要是编译器的参数,可以使用ctrl+space来查看有哪些可用参数;
也可以在configurations中存在鼠标光标的情况下,点击右下自动出现的Add Configurations按钮;
为什么选gdb不选 windows?因为这个不会执行预任务,也就没法编译文件了;
为什么选 launch不选attach,是因为attach用来给正在执行的文件用的,比如网页中的组件,而launch是执行新文件。
// launch.json
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "(gdb) Launch", //这个应该是F1中出现的名字
"preLaunchTask": "Build", //在launch之前运行的任务名,这个名字一定要跟tasks.json中的任务名字大小写一致
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${fileDirname}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe", //需要运行的是当前打开文件的目录中,名字和当前文件相同,但扩展名为exe的程序
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false, // 选为true则会在打开控制台后停滞,暂时不执行程序
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}", // 当前工作路径:当前文件所在的工作空间
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": true, // 是否使用外部控制台,选false的话,我的vscode会出现错误
"MIMode": "gdb",
"miDebuggerPath": "F:\\MinGW\\bin\\gdb.exe",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
}]
}
下面的json文件配置是另外一种,试过可以,但是在Add Configuration中没有这一种选项可选。(这里记录存档一下配置文件内容)
//launch.json
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
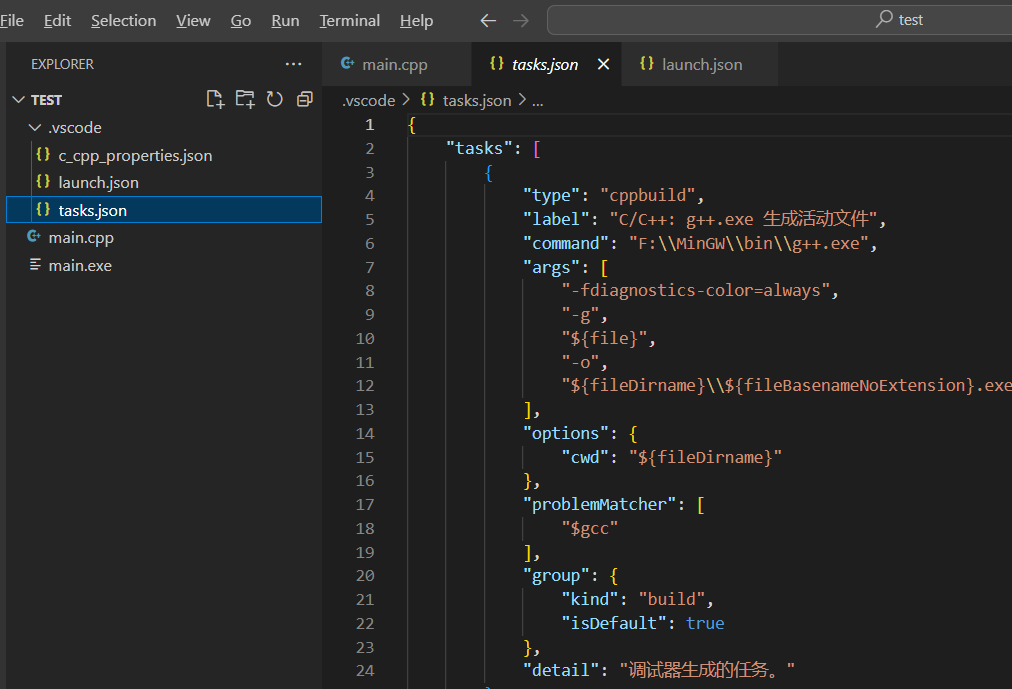
"name": "g++.exe - 生成和调试活动文件",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${fileDirname}\\${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${fileDirname}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": true, // 此处默认为false不弹出控制台窗口,修改为true,使其弹出控制台窗口
"MIMode": "gdb",
"miDebuggerPath": "F:\\MinGW\\bin\\gdb.exe",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "为 gdb 启用整齐打印",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
],
"preLaunchTask": "C/C++: g++.exe 生成活动文件"
}
]
}
在launch.json文件中,把midebuggerpath改成dbg的路径,dbg在MinGW安装路径下的bin文件夹中,然后将"externalConsole": false的值建议改成true,这个是运行的时候会不会弹出黑框,默认是不弹出。
测试文件运行成功之后显示(F5运行):
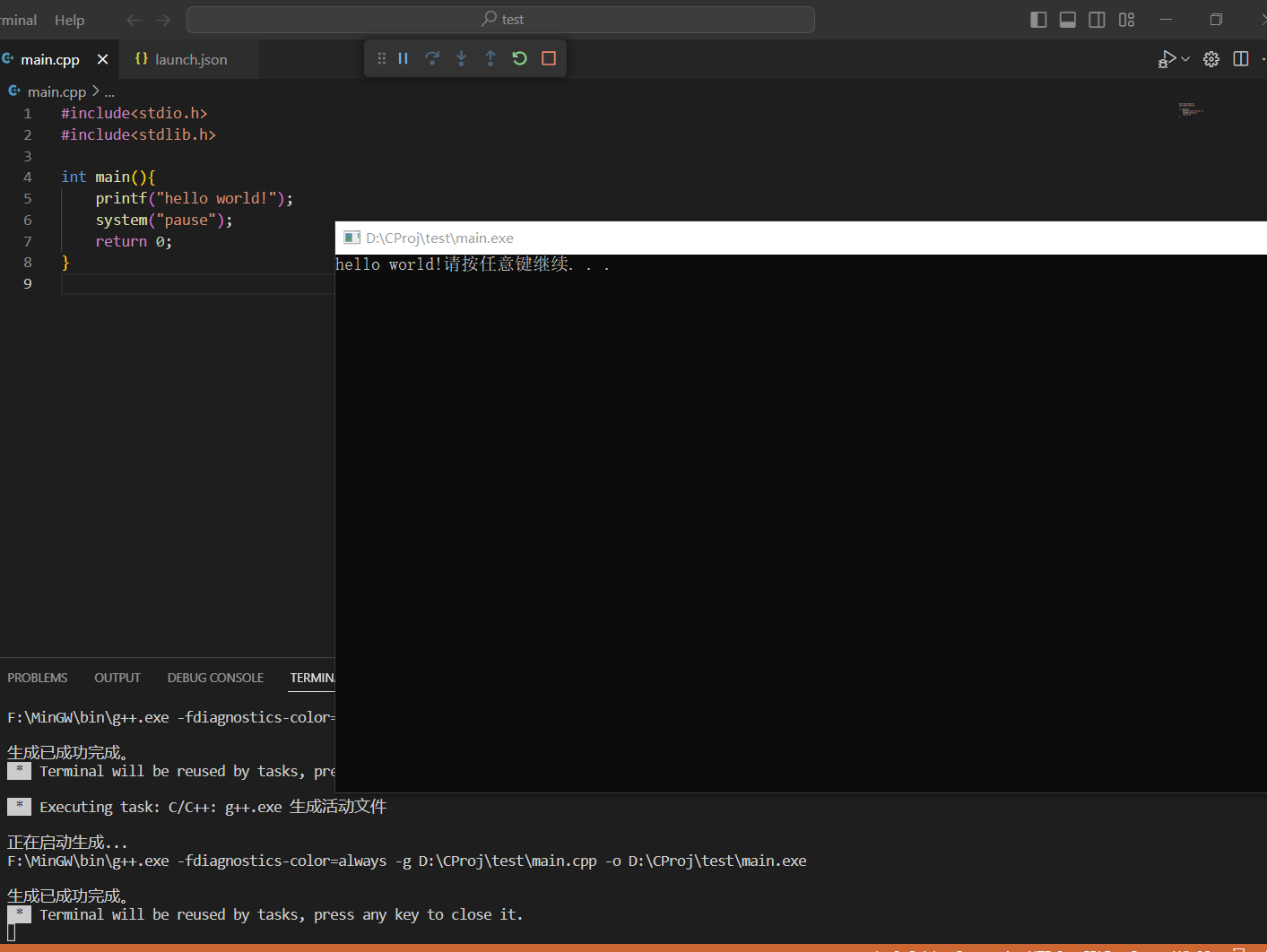
到这里就可以正常运行了!!
方法2:使用Native Debug插件

使用这个插件可以简单化配置流程。
在选择环境时选择:C++(GDB/LLDB);
在选择配置时选择:g++.exe build and debug active file;
在选择task时选择:g++.exe build active file。
方法3:使用C/C++ Compile Run插件
VSCode的这个插件更简单,但只能用于单文件。
这下根本无需配置task.json和launch.json,保存后直接按F6自动编译运行,其他功能见插件下载页的how to use。
Native Debug插件和C/C++ Compile Run插件的对比:
前者更通用(可用于多种编译语言),后者更简单。
VSCode的其他环境配置(暂时没用到,先用于记录)
Rust(使用Native Debug插件)
首选选择左侧的dubug选项,在debug界面下点击选项(绿色箭头右边的齿轮图案),在下拉框选择GDB,进入到luanch.json文件中将target的值改为”./target/debug/${workspaceFolderBasename}.exe”,并且增加一个参数值"prelaunchTask": "Build";
//tasks.json
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "Build",
"type": "shell",
"command": "cargo build"
}
]
}
其次点击运行会发现没有Build,选择”Create tasks.json file from template”, 出现可选的模板后选择”Others”, 在tasks.json文件中将”command”参数的值改为”cargo build”, 将”label”参数的值改为”Build”,这样就可以成功debug了。
// launch.json
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Debug",
"type": "gdb", // 使用Native Debug插件提供的gdb类型
"request": "launch",
"target": "./target/debug/${workspaceFolderBasename}.exe", // 注意这里使用了第五部分讲到的配置变量
"preLaunchTask": "Build",
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}",
"valuesFormatting": "parseText"
}
]
}
Typescript(用于写VSCode插件时的项目设置)
tasks.json
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"type": "npm",
"script": "watch",
"problemMatcher": "$tsc-watch",
"isBackground": true,
"presentation": {
"reveal": "never"
},
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
}
}
]
}
launch.json
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Run Extension",
"type": "extensionHost",
"request": "launch",
"runtimeExecutable": "${execPath}",
"args": [
"--extensionDevelopmentPath=${workspaceFolder}"
],
"outFiles": [
"${workspaceFolder}/out/**/*.js"
],
"preLaunchTask": "${defaultBuildTask}"
},
{
"name": "Extension Tests",
"type": "extensionHost",
"request": "launch",
"runtimeExecutable": "${execPath}",
"args": [
"--extensionDevelopmentPath=${workspaceFolder}",
"--extensionTestsPath=${workspaceFolder}/out/test/suite/index"
],
"outFiles": [
"${workspaceFolder}/out/test/**/*.js"
],
"preLaunchTask": "${defaultBuildTask}"
}
]
}
一些常用的预定义变量
支持下面的预定义变量:
${workspaceFolder}- 当前工作目录(根目录)${workspaceFolderBasename}- 当前文件的父目录${file}- 当前打开的文件名(完整路径)${relativeFile}- 当前根目录到当前打开文件的相对路径(包括文件名)${relativeFileDirname}- 当前根目录到当前打开文件的相对路径(不包括文件名)${fileBasename}- 当前打开的文件名(包括扩展名)${fileBasenameNoExtension}- 当前打开的文件名(不包括扩展名)${fileDirname}- 当前打开文件的目录${fileExtname}- 当前打开文件的扩展名${cwd}- 启动时task工作的目录${lineNumber}- 当前激活文件所选行${selectedText}- 当前激活文件中所选择的文本${execPath}- vscode执行文件所在的目录${defaultBuildTask}- 默认编译任务(build task)的名字
预定义变量示例:
假设你满足以下的条件
一个文件 /home/your-username/your-project/folder/file.ext 在你的编辑器中打开;
一个目录 /home/your-username/your-project 作为你的根目录。
下面的预定义变量则代表:
${workspaceFolder}-/home/your-username/your-project${workspaceFolderBasename}-your-project${file}-/home/your-username/your-project/folder/file.ext${relativeFile}-folder/file.ext${relativeFileDirname}-folder${fileBasename}- file.ext${fileBasenameNoExtension}-file${fileDirname}-/home/your-username/your-project/folder${fileExtname}-.ext${lineNumber}- 光标所在行${selectedText}- 编辑器中所选择的文本${execPath}- Code.exe的位置
Tip: vscode的智能提示会在tasks.json和launch.json 提示所有支持的预定义变量。
参考链接:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/92175757?utm_id=0